L. W. Rogers Building: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (54 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Rogers_Building_1a.jpg|570px|thumb|right|L. W. Rogers Building, front view, 2007. Photographer Jeff Gresko. Image from the Theosophical Society in America Archives.]] | [[File:Rogers_Building_1a.jpg|570px|thumb|right|L. W. Rogers Building, front view, 2007. Photographer Jeff Gresko. Image from the Theosophical Society in America Archives.]] | ||
The '''L. W. Rogers Building''' is the headquarters of the [[Theosophical Society in America]], located on the [[Olcott (campus)|Olcott campus]] in Wheaton, Illinois. It houses the business offices, auditorium, classroom, meditation room, staff residences, guest rooms, and the [[Henry S. Olcott Memorial Library]]. | The '''L. W. Rogers Building''' is the headquarters of the [[Theosophical Society in America]], located on the [[Olcott (campus)|Olcott campus]] in Wheaton, Illinois. It houses the business offices, auditorium, classroom, meditation room, staff residences, guest rooms, and the [[Henry S. Olcott Memorial Library]]. The building came to be named after [[L. W. Rogers]], during whose term as Theosophical Society president it was built. | ||
See more of the building in a video '''[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IFXPgUdWdHw#t=60 The Theosophical Society in America: A Brief Tour]'''. | |||
== History == | == History == | ||
[[File:Rogers_at_desk_1927.jpg|200px|thumb|right|L. | [[File:Rogers_at_desk_1927.jpg|200px|thumb|right|L. W. Rogers at his desk in 1927. Image from TSA Archives.]] | ||
In 1925 the [[American Theosophical Society]], now known as the [[Theosophical Society in America]], purchased land in Wheaton, Illinois for a new headquarters campus. The Board of Directors approached architect [[Claude Bragdon]], a prominent member of the Society, to design a building to serve as the national administrative center. Bragdon was then closing down his architectural practice to begin a career in theatrical design, and recommended a Chicago architect, Irving Kane Pond, of Pond & Pond, Martin & Lloyd, to take on the project. The architectural firm submitted two designs, and the Board could not decide between them, so President [[L. W. Rogers]] sent the drawings to Bragdon for review. Bragdon wired back that he preferred the asymmetrical design by Irving Pond over a symmetrical rendering by one of his partners.<ref>Claude Bragdon telegram to L. W. Rogers, | In 1925 the [[American Theosophical Society]], now known as the [[Theosophical Society in America]], purchased land in Wheaton, Illinois for a new headquarters campus. The Board of Directors approached architect [[Claude Bragdon]], a prominent member of the Society, to design a building to serve as the national administrative center. Bragdon was then closing down his architectural practice to begin a career in theatrical design, and recommended a Chicago architect, '''Irving Kane Pond''', of Pond & Pond, Martin & Lloyd, to take on the project. The architectural firm submitted two designs, and the Board could not decide between them, so President [[L. W. Rogers]] sent the drawings to Bragdon for review. Bragdon wired back that he preferred the asymmetrical design by Irving Pond over a symmetrical rendering by one of his partners.<ref>Claude Bragdon telegram to L. W. Rogers, 1926, TSA Archives.</ref> | ||
The drawings from Irving Kane Pond's proposal were published in [[The Messenger (periodical)|''The Messenger'']], and the members were excited to see them. The original art works were created with pen and pastels. Along with blueprints, correspondence, and specifications, they have been preserved using grant funding from the '''Illinois State Historical Records Advisory Board''' by the Archives Department of the [[Henry S. Olcott Memorial Library]]. | |||
<gallery widths="140px" heights="100px" perrow="5"> | |||
File:Headquarters view from southeast.jpg|Headquarters from southeast | |||
File:Reception Hall.jpg|Reception hall | |||
File:Library.jpg|Library | |||
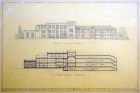
File:Front Elevation.jpg|Front Elevation | |||
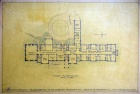
File:First Floor Plan.jpg|First Floor Plan | |||
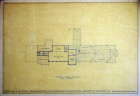
File:Second Floor Plan.jpg|Second Floor Plan | |||
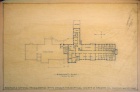
File:Third Floor Plan.jpg|Third Floor Plan | |||
File:Basement Plan.jpg|Basement Plan | |||
File:Irving Kane Pond initials.jpg|Irving Kane Pond signature | |||
</gallery> | |||
== | == Cornerstone ceremony == | ||
[[File:Cornerstone_crowd.jpg|250px|thumb|left|Crowds at cornerstone ceremony.]] | |||
[[File:Cornerstone_1.jpg|250px|thumb|right|Annie Besant in cornerstone ceremony.]] | |||
[[File:Cornerstone_parchment.jpg|200px|right|thumb|Parchment sealed in cornerstone]] | |||
Construction began in 1926, and the cornerstone was laid on Sunday, [[August 29|August 29th]] in a [[Co-Freemasonry|Co-Masonic]] ceremony led by [[Annie Besant]]. The event was heavily covered by the ''Chicago Tribune'' and other newspapers, and people came by the hundreds on the interurban trains from Chicago to be present. In the photograph at the right, Annie Besant and [[A. P. Warrington]] are in front; [[L. W. Rogers]] appears between them; and architect '''Irving Kane Pond''' is third from the right (older man in dark suit). [[Jiddu Krishnamurti]] accompanied Annie Besant to Wheaton, but he does not appear in photographs of the ceremony. The architect mentioned the event in his autobiography. The cornerstone was filled with copies of major Theosophical texts such as ''The Secret Doctrine''. Also enclosed was a parchment signed by L. W. Rogers, vice president C. T. Holland, and the directors of the Board: Maude N. Couch, M. B. Hudson, E. C. Boxell, and H. Kay Campbell. Many prominent Theosophists were present, including [[Marie Poutz]], Albert Schwartz, [[Irving S. Cooper]], and [[Beatrice Wood]]. | |||
The cornerstone ceremony was featured in a '''[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wH-vuNwK3RU 1926 silent film]''' that is available on YouTube. | |||
[ | <br> | ||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
== Dedication ceremony == | |||
A dedication ceremony was conducted by the international president of the Theosophical Society, [[George S. Arundale]] | A dedication ceremony was conducted by the international president of the Theosophical Society, [[George S. Arundale]] on [[August 28]], 1927. He appears in the middle of the photograph below that appeared in the ''Chicago Tribune''. His wife [[Rukmini Devi Arundale|Rukmini Devi]] and L. W. Rogers are at the left, and A. P. Warrington at the far right. On [[September 17|September 17th]] the staff moved their offices and residences from Chicago. | ||
[[File:Rogers_Building_Dedication_2.jpg|260px|thumb|center|Dedication, August 28, 1927.]] | |||
== Architecture == | == Architecture == | ||
[[File:Rogers Building | [[File:Rogers Building from northeast 1931.jpg|280px|left|thumb|Rogers Building in 1931, from northeast]] | ||
The architecture of Irving Kane Pond is difficult to classify, but the Rogers Building is generally considered to be Collegiate Gothic in style, with interiors influenced by the Arts and Crafts Movement. The exterior was constructed of Bedford limestone and red brick, with a carved stone lintel over the main entrance. | |||
The architecture of Irving Kane Pond is difficult to classify, but the Rogers Building is generally considered to be Collegiate Gothic in style, with interiors influenced by the Arts and Crafts Movement. The exterior was constructed of Bedford limestone and red brick, with a carved stone lintel over the main entrance. The original roof was a mixture of purple and green slates.The building's asymmetrical design helps to create an impression that the building evolved organically over time, adjusting to the needs of its inhabitants. In point of fact, the exterior appearance has hardly changed over the years, and most spaces in the building are still used for the same functions they were designed to support. Architectural elements on the exterior include horizontal band courses, dentils, and decorative windows. Inside, most rooms are accented simply with dark wood. The three areas with more interesting design features are the lobby, the library, and the meditation room. | |||
The original roof was a mixture of purple and green slates. The building's asymmetrical design helps to create an impression that the building evolved organically over time, adjusting to the needs of its inhabitants. In point of fact, the exterior appearance has hardly changed over the years, and most spaces in the building are still used for the same functions they were designed to support. Architectural elements on the exterior include horizontal band courses, dentils, and decorative windows. Inside, most rooms are accented simply with dark wood. The three areas with more interesting design features are the lobby, the library, and the meditation room. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
== Photo gallery of construction and 1920s exteriors == | |||
<gallery widths="140px" heights="100px" perrow="5"> | |||
File:Construction1 1926 from SE.jpg|Construction site, taken from southeast in 1926 | |||
File:Construction2 1927 from SE.jpg|View from southeast in 1927 | |||
File:Construction3 from west July 1927.jpg|View from west in 1927 | |||
File:Construction4_from_NW_Jul_27_1927.jpg|View from northwest, July 27, 1927 | |||
File:From east 1927.jpg|View from east in 1927 | |||
File:Construction5_from_NE_July_1927.jpg|View from northeast, July, 1927 | |||
File:View from ESE with new driveway.jpg|View from east southeast, late in 1927 | |||
File:Rear view late 1920s.jpg|View from west, late 1920s | |||
File:Rogers Building from NW.jpg|View from northwest, late 1920s | |||
</gallery> | |||
== Photo gallery of 1920s interiors == | == Photo gallery of 1920s interiors == | ||
<gallery> | <gallery widths="140px" heights="100px" perrow="5"> | ||
File:Reception Hall 1.jpg|Reception hall | File:Reception Hall 1.jpg|Reception hall | ||
File:Reception Hall 2 .jpg|Reception hall | File:Reception Hall 2 .jpg|Reception hall | ||
| Line 39: | Line 76: | ||
== Lobby and murals == | == Lobby and murals == | ||
The lobby is a open two-story space with entrances on the east and west. An oriel window permits the President's secretary to see visitors from above. The outstanding feature of the lobby is the [[Murals at Olcott (art work)|mural]] painted by [[Richard Blossom Farley]] on commission from Theosophist and arts patron [[Georgine Shillard-Smith]]. | The lobby is a open two-story space with entrances on the east and west. An oriel window permits the President's secretary to see visitors from above. The outstanding feature of the lobby is the '''[[Murals at Olcott (art work)|mural]]''' painted by [[Richard Blossom Farley]] on commission from Theosophist and arts patron [[Georgine Shillard-Smith]]. | ||
== Meditation room == | == Meditation room == | ||
The meditation room is a serene space used only for meditation or meditation classes. Staff members gather every morning at 8:30 for 15 minutes for a group practice, and a healing group meets each Wednesday evening. Beautiful art works and oriental carpets line the room, including a thanka presented by the Dalai Lama in 1981 and a painting of Helena Petrovna Blavatsky by [[Gutzon Borglum]], sculptor of Mount Rushmore. Just outside the doors of the meditation room are two pastels by Theosophist [[Burton Callicott]] They are [[Mandorla (art work)|''Mandorla'']] and [[Antahkarana (art work)|''Antahkarana'']] | The meditation room is a serene space used only for meditation or meditation classes. Staff members gather every morning at 8:30 for 15 minutes for a group practice, and a healing group meets each Wednesday evening. Beautiful art works and oriental carpets line the room, including a thanka presented by the [[Tenzin Gyatso, the XIV Dalai Lama|Dalai Lama]] in 1981 and a painting of Helena Petrovna Blavatsky by [[Gutzon Borglum]], sculptor of Mount Rushmore. Just outside the doors of the meditation room are two pastels by Theosophist [[Burton Callicott]] They are [[Mandorla (art work)|''Mandorla'']] and [[Antahkarana (art work)|''Antahkarana'']]. | ||
== Library == | == Library == | ||
[[File:Library_reading_room.jpg| | [[File:Library_reading_room.jpg|200px|thumb|right|Library reading room]] | ||
The [[Henry S. Olcott Memorial Library]], formerly known as the [[Olcott Library and Research Center]], is a beautiful space that is used for meetings and performances as well as traditional library activities. The library was expanded in 1964 to add space on three levels. The architects were Theosophists Lillian and Wilbur Leenhouts of Milwaukee. | The [[Henry S. Olcott Memorial Library]], formerly known as the [[Olcott Library and Research Center]], is a beautiful space that is used for meetings and performances as well as traditional library activities. The library was expanded in 1964 to add space on three levels. The architects were Theosophists Lillian and Wilbur Leenhouts of Milwaukee. | ||
<br> | |||
== Auditorium == | == Auditorium == | ||
[[File:Auditorium.jpg| | [[File:Auditorium.jpg|200px|left|thumb|Auditorium]] | ||
The third-floor auditorium is used for lectures, workshops, yoga classes, conferences, and numerous other activities throughout the year. The space was remodeled in 2009, benefiting from the Bland administration's Capital Funds Campaign. A column was removed to improve sight-lines for the audience. The sub-floor was rebuilt and new carpeting was installed. Co-Masons donated a beautiful door and door frame featuring stained glass with the Society's emblem etched into it. New audiovisual equipment was installed to support Webcasts and recording of programs. | |||
The | The anteroom to the auditorium was established as the '''Olcott Gallery''' during the administration of [[John Algeo]]. Exhibits were changed quarterly, with the artists are announced in [[The Quest (periodical)|''Quest'' magazine]]. In recent years a permanent display of photos has filled the gallery. | ||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
== Art | == Art works on permanent display == | ||
[[File:Krishnamurti painting.jpg|130px|right|thumb|J. Krishnamurti portrait. Painted from a photograph in 1926 by Henry Schwartz.]] | |||
Numerous paintings, sculptures, Buddhist thankas, and oriental rugs decorate the building. Some of the most prominent works include: | |||
* Madonna by Italian Renaissance painter Il Morreto (Alessandro Bonvicino, 1498-1554), in library. | |||
* [[Schwartz Portrait of Krishnamurti (art work)|Portrait]] of [[Jiddu Krishnamurti]], by Henry Schwartz, in second-floor hall. | |||
* Three paintings, ''Demon Queller'', ''Toys'', and ''Suffering Fools'', by [[Don Kruse]], temporarily in storage. | |||
* Portrait of H. P. Blavatsky by [[Gutzon Borglum]], in Meditation Room. | |||
* [[Antahkarana (art work)|''Antahkarana'']], pastel by [[Burton Callicott]], by Meditation Room door. | |||
* [[Mandorla (art work)|''Mandorla'']], pastel by [[Burton Callicott]], by Meditation Room door. | |||
* [[Mandorla No. 12 (art work)|''Mandorla No. 12'']], painting by [[Burton Callicott]], in staircase to auditorium. | |||
* ''Tantric Circle'' sculpture, by Michael Cullen Todd, 1985, on front lawn. | |||
* ''Slant'' sculpture, by David Middlebrook, 1984, on front lawn. | |||
* Thanka donated by [[Dalai Lama]], 1981, in Meditation Room. | |||
* Portrait of [[Charles Webster Leadbeater|C. W. Leadbeater]] by [[Erling Roberts]], temporarily in storage. | |||
* [[The Three Objects (art work)|''The Three Objects'']], 1944, calligraphy by [[A. Theodore Bondy]], in second-floor hall. | |||
* Bust of [[Annie Besant]] by D. R. Choudhri, 1935, in second-floor hall. | |||
* Drypoint etching ''Buddha Serenity'' by Bertha Jaques, 1934, in Member Services office. | |||
* Painting ''Toward the Light'' by [[E. L. Thomson]], in Webinar Department office. | |||
Buddhist scholar Glenn Mullin created a video tour called [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Jaoly96xxBw Buddhist Art at the Theosophical Society in America]. | |||
== Kitchen and dining room == | == Kitchen and dining room == | ||
In 2010, the basement kitchen and dining area were extensively remodeled. The dining room was renamed Nicholson Hall in honor of the Nicholson family whose generous donation made the renovation possible. | In 2010, the basement kitchen and dining area were extensively remodeled. The dining room was renamed '''Nicholson Hall''' in honor of the Nicholson family whose generous donation made the renovation possible. | ||
== | == Guest rooms == | ||
[[File:Guest room.jpg|right|180px|thumb|Guest room]] | |||
Guest rooms are available at modest cost for visitors such as lecturers, board members, and academic researchers. The building was designed to provide housing for staff members, and since September 1927, there have always been some employees living there. | |||
== | == Additional resources == | ||
=== Articles === | === Articles === | ||
*[ | * [https://www.theosophical.org/publications/quest-magazine/coloring-in-the-lines-around-my-think?highlight=WyJrcnVzZSJd Coloring in the Lines around My Think] by Don Kruse. This is an article by an artist who donated paintings that hang in the building. | ||
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Irving_Kane_Pond Irving Kane Pond] in Wikipedia. | |||
== | === Video === | ||
* '''[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IFXPgUdWdHw#t=60 The Theosophical Society in America: A Brief Tour]'''. Posted on YouTube on June 13, 2012. Narrated by Tim Boyd. | |||
* '''[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wH-vuNwK3RU 40th Annual Convention of the American Theosophical Society]'''. Highlights of the 1926 annual convention in Chicago, including cornerstone ceremony for the new headquarters building. | |||
* '''[http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Jaoly96xxBw Buddhist Art at the Theosophical Society in America]'''. A tour of the Buddhist art in the building, as described by Buddhist scholar Glenn Mullin. | |||
=== Archival materials === | |||
*Theosophical Society in America '''Archives Department''' has architect's drawings, 1926 blueprints, correspondence, and detailed specifications for each subcontractor (plumbing, roofing, etc.) | * Theosophical Society in America '''Archives Department''' has architect's drawings, 1926 blueprints, correspondence, and detailed specifications for each subcontractor (plumbing, roofing, etc.). See Records Series 09.04.01 for Rogers Building Construction Records, and series 43 for Blue prints and Architectural Renderings. | ||
== Notes == | == Notes == | ||
Latest revision as of 22:23, 31 March 2024
The L. W. Rogers Building is the headquarters of the Theosophical Society in America, located on the Olcott campus in Wheaton, Illinois. It houses the business offices, auditorium, classroom, meditation room, staff residences, guest rooms, and the Henry S. Olcott Memorial Library. The building came to be named after L. W. Rogers, during whose term as Theosophical Society president it was built.
See more of the building in a video The Theosophical Society in America: A Brief Tour.
History
In 1925 the American Theosophical Society, now known as the Theosophical Society in America, purchased land in Wheaton, Illinois for a new headquarters campus. The Board of Directors approached architect Claude Bragdon, a prominent member of the Society, to design a building to serve as the national administrative center. Bragdon was then closing down his architectural practice to begin a career in theatrical design, and recommended a Chicago architect, Irving Kane Pond, of Pond & Pond, Martin & Lloyd, to take on the project. The architectural firm submitted two designs, and the Board could not decide between them, so President L. W. Rogers sent the drawings to Bragdon for review. Bragdon wired back that he preferred the asymmetrical design by Irving Pond over a symmetrical rendering by one of his partners.[1]
The drawings from Irving Kane Pond's proposal were published in The Messenger, and the members were excited to see them. The original art works were created with pen and pastels. Along with blueprints, correspondence, and specifications, they have been preserved using grant funding from the Illinois State Historical Records Advisory Board by the Archives Department of the Henry S. Olcott Memorial Library.
Cornerstone ceremony
Construction began in 1926, and the cornerstone was laid on Sunday, August 29th in a Co-Masonic ceremony led by Annie Besant. The event was heavily covered by the Chicago Tribune and other newspapers, and people came by the hundreds on the interurban trains from Chicago to be present. In the photograph at the right, Annie Besant and A. P. Warrington are in front; L. W. Rogers appears between them; and architect Irving Kane Pond is third from the right (older man in dark suit). Jiddu Krishnamurti accompanied Annie Besant to Wheaton, but he does not appear in photographs of the ceremony. The architect mentioned the event in his autobiography. The cornerstone was filled with copies of major Theosophical texts such as The Secret Doctrine. Also enclosed was a parchment signed by L. W. Rogers, vice president C. T. Holland, and the directors of the Board: Maude N. Couch, M. B. Hudson, E. C. Boxell, and H. Kay Campbell. Many prominent Theosophists were present, including Marie Poutz, Albert Schwartz, Irving S. Cooper, and Beatrice Wood.
The cornerstone ceremony was featured in a 1926 silent film that is available on YouTube.
Dedication ceremony
A dedication ceremony was conducted by the international president of the Theosophical Society, George S. Arundale on August 28, 1927. He appears in the middle of the photograph below that appeared in the Chicago Tribune. His wife Rukmini Devi and L. W. Rogers are at the left, and A. P. Warrington at the far right. On September 17th the staff moved their offices and residences from Chicago.
Architecture
The architecture of Irving Kane Pond is difficult to classify, but the Rogers Building is generally considered to be Collegiate Gothic in style, with interiors influenced by the Arts and Crafts Movement. The exterior was constructed of Bedford limestone and red brick, with a carved stone lintel over the main entrance.
The original roof was a mixture of purple and green slates. The building's asymmetrical design helps to create an impression that the building evolved organically over time, adjusting to the needs of its inhabitants. In point of fact, the exterior appearance has hardly changed over the years, and most spaces in the building are still used for the same functions they were designed to support. Architectural elements on the exterior include horizontal band courses, dentils, and decorative windows. Inside, most rooms are accented simply with dark wood. The three areas with more interesting design features are the lobby, the library, and the meditation room.
Photo gallery of construction and 1920s exteriors
Photo gallery of 1920s interiors
Lobby and murals
The lobby is a open two-story space with entrances on the east and west. An oriel window permits the President's secretary to see visitors from above. The outstanding feature of the lobby is the mural painted by Richard Blossom Farley on commission from Theosophist and arts patron Georgine Shillard-Smith.
Meditation room
The meditation room is a serene space used only for meditation or meditation classes. Staff members gather every morning at 8:30 for 15 minutes for a group practice, and a healing group meets each Wednesday evening. Beautiful art works and oriental carpets line the room, including a thanka presented by the Dalai Lama in 1981 and a painting of Helena Petrovna Blavatsky by Gutzon Borglum, sculptor of Mount Rushmore. Just outside the doors of the meditation room are two pastels by Theosophist Burton Callicott They are Mandorla and Antahkarana.
Library
The Henry S. Olcott Memorial Library, formerly known as the Olcott Library and Research Center, is a beautiful space that is used for meetings and performances as well as traditional library activities. The library was expanded in 1964 to add space on three levels. The architects were Theosophists Lillian and Wilbur Leenhouts of Milwaukee.
Auditorium
The third-floor auditorium is used for lectures, workshops, yoga classes, conferences, and numerous other activities throughout the year. The space was remodeled in 2009, benefiting from the Bland administration's Capital Funds Campaign. A column was removed to improve sight-lines for the audience. The sub-floor was rebuilt and new carpeting was installed. Co-Masons donated a beautiful door and door frame featuring stained glass with the Society's emblem etched into it. New audiovisual equipment was installed to support Webcasts and recording of programs.
The anteroom to the auditorium was established as the Olcott Gallery during the administration of John Algeo. Exhibits were changed quarterly, with the artists are announced in Quest magazine. In recent years a permanent display of photos has filled the gallery.
Art works on permanent display
Numerous paintings, sculptures, Buddhist thankas, and oriental rugs decorate the building. Some of the most prominent works include:
- Madonna by Italian Renaissance painter Il Morreto (Alessandro Bonvicino, 1498-1554), in library.
- Portrait of Jiddu Krishnamurti, by Henry Schwartz, in second-floor hall.
- Three paintings, Demon Queller, Toys, and Suffering Fools, by Don Kruse, temporarily in storage.
- Portrait of H. P. Blavatsky by Gutzon Borglum, in Meditation Room.
- Antahkarana, pastel by Burton Callicott, by Meditation Room door.
- Mandorla, pastel by Burton Callicott, by Meditation Room door.
- Mandorla No. 12, painting by Burton Callicott, in staircase to auditorium.
- Tantric Circle sculpture, by Michael Cullen Todd, 1985, on front lawn.
- Slant sculpture, by David Middlebrook, 1984, on front lawn.
- Thanka donated by Dalai Lama, 1981, in Meditation Room.
- Portrait of C. W. Leadbeater by Erling Roberts, temporarily in storage.
- The Three Objects, 1944, calligraphy by A. Theodore Bondy, in second-floor hall.
- Bust of Annie Besant by D. R. Choudhri, 1935, in second-floor hall.
- Drypoint etching Buddha Serenity by Bertha Jaques, 1934, in Member Services office.
- Painting Toward the Light by E. L. Thomson, in Webinar Department office.
Buddhist scholar Glenn Mullin created a video tour called Buddhist Art at the Theosophical Society in America.
Kitchen and dining room
In 2010, the basement kitchen and dining area were extensively remodeled. The dining room was renamed Nicholson Hall in honor of the Nicholson family whose generous donation made the renovation possible.
Guest rooms
Guest rooms are available at modest cost for visitors such as lecturers, board members, and academic researchers. The building was designed to provide housing for staff members, and since September 1927, there have always been some employees living there.
Additional resources
Articles
- Coloring in the Lines around My Think by Don Kruse. This is an article by an artist who donated paintings that hang in the building.
- Irving Kane Pond in Wikipedia.
Video
- The Theosophical Society in America: A Brief Tour. Posted on YouTube on June 13, 2012. Narrated by Tim Boyd.
- 40th Annual Convention of the American Theosophical Society. Highlights of the 1926 annual convention in Chicago, including cornerstone ceremony for the new headquarters building.
- Buddhist Art at the Theosophical Society in America. A tour of the Buddhist art in the building, as described by Buddhist scholar Glenn Mullin.
Archival materials
- Theosophical Society in America Archives Department has architect's drawings, 1926 blueprints, correspondence, and detailed specifications for each subcontractor (plumbing, roofing, etc.). See Records Series 09.04.01 for Rogers Building Construction Records, and series 43 for Blue prints and Architectural Renderings.
Notes
- ↑ Claude Bragdon telegram to L. W. Rogers, 1926, TSA Archives.