Young Men's Indian Association: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[File:YMIA Building entrance.jpg|right|350px|thumb|Entrance to YMIA Building, Chennai]] | [[File:YMIA Building entrance.jpg|right|350px|thumb|Entrance to YMIA Building, Chennai]] | ||
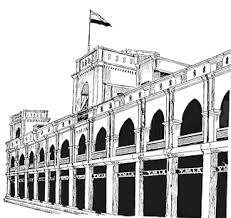
The '''Young Men's Indian Association''' (YMIA) is a youth organization that was founded by [[Annie Besant]] in 1914 in support of the Indian independence movement. | The '''Young Men's Indian Association''' (YMIA) is a youth organization that was founded by [[Annie Besant]] in 1914 in support of the Indian independence movement. In 1915 she built Gokhale Hall, named after [[Gopal Krishna Gokhale]], so serve as its headquarters. YMIA continues to be a prominent institution in Chennai, offering Indian youth opportunities to improve in body, mind, moral character, and citizenship.<ref>[http://www.ymiaindia.com/history.html# YMIA web page]</ref><ref>Madras High Court document. 1962. Citation: AIR 1964 Mad 63, 1963 14 STC 1030 Mad Available at [http://www.indiankanoon.org/doc/1389145/ IndianKanoon.org].</ref> It offers recreational facilities, lectures, library and reading room, and residences. The YMIA has a [http://www.ymiaindia.com/index.html web page] and a presence in [https://www.facebook.com/pages/Young-Mens-Indian-Association/780448362021235 Facebook]. | ||
== Early history == | == Early history == | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
By 1914, Annie Besant had already been working for some years on establishment of schools and organizations to support Indian education and nationalism. In a 1908 address at Central Hindu College, she said, "Our work is the training of thousands of India's sons into noble manhood into worthiness to become free citizens in a free land." <ref>Annie Besant, ''The Besant Spirit Volume 7: The India that Shall Be: Articles from New India.''</ref> Her political activity reached greatest intensity in the years 1914-1917. She worked with several other nationalist leaders to demand home rule for India, and formation of the YMIA was one aspect of this movement. | By 1914, Annie Besant had already been working for some years on establishment of schools and organizations to support Indian education and nationalism. In a 1908 address at Central Hindu College, she said, "Our work is the training of thousands of India's sons into noble manhood into worthiness to become free citizens in a free land." <ref>Annie Besant, ''The Besant Spirit Volume 7: The India that Shall Be: Articles from New India.''</ref> Her political activity reached greatest intensity in the years 1914-1917. She worked with several other nationalist leaders to demand home rule for India, and formation of the YMIA was one aspect of this movement. | ||
Mrs. Besant sponsored the construction of a building in Madras (now Chennai) for the YMIA, which was completed in 1915. A large public meeting hall in the building, designed to seat 1500 people, was given the name Gopal Krishna Gokhale Hall after the Indian leader. When she announced the formation of the [[Home Rule League]] in 1916, it was at '''Gokhale Hall'''. Many other nationalistic events took place there. The Indian Society of Oriental Art held an exhibition at the YMIA building in 1916, organized by Theosophist [[James Cousins]].<ref>Kathleen Taylor, ''Sir John Woodroffe Tantra and Bengal: 'An Indian Soul in a European Body?''' (Surrey: Routledge, 2012), 70.</ref> | Mrs. Besant sponsored the construction of a building in Madras (now Chennai) for the YMIA, which was completed in 1915. A large public meeting hall in the building, designed to seat 1500 people, was given the name Gopal Krishna Gokhale Hall after the Indian leader. When she announced the formation of the [[Home Rule League]] in 1916, it was at '''Gokhale Hall'''. Many other nationalistic events took place there. The '''Indian Society of Oriental Art''' held an exhibition at the YMIA building in 1916, organized by Theosophist [[James Cousins]].<ref>Kathleen Taylor, ''Sir John Woodroffe Tantra and Bengal: 'An Indian Soul in a European Body?''' (Surrey: Routledge, 2012), 70.</ref> | ||
In his introduction to ''The Besant Spirit'', [[George S. Arundale]] wrote of Dr. Besant's daily routine in Adyar during the time of her great activism in the Indian independence movement. Each evening at 5:30, | In his introduction to ''The Besant Spirit'', [[George S. Arundale]] wrote of Dr. Besant's daily routine in Adyar during the time of her great activism in the Indian independence movement. Each evening at 5:30, | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
== Objects of the Association == | == Objects of the Association == | ||
According to | According to its web page, the Association has these objects: | ||
* To provide a building or buildings as a Young Men’s Club, with gymnasium, lecture hall, library, reading-room, recreation-rooms and residential quarters, mainly for students. | * To provide a building or buildings as a Young Men’s Club, with gymnasium, lecture hall, library, reading-room, recreation-rooms and residential quarters, mainly for students. | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
== Facilities == | == Facilities == | ||
YMIA has two locations in Chennai: the registered office at New India Buildings at No.49 Moore Street, and administrative office at 54-57/2 Royapettah High Road in Mylapore. Gokhale Hall was partially demolished, but is now being renovated. Two hostels are now serving about 150 youth. Over the years additional hostels were operated in George town, Triplicane, Mylapore, and Nungambakkam, but these had to be closed despite their popularity.<ref>Young Men's Indian Association [http://www.ymiaindia.com/history.html# web page].</ref> | YMIA has two locations in Chennai: the registered office at New India Buildings at No.49 Moore Street, and the administrative office at 54-57/2 Royapettah High Road in Mylapore. Gokhale Hall was partially demolished, but is now being renovated. Two hostels are now serving about 150 youth. Over the years additional hostels were operated in George town, Triplicane, Mylapore, and Nungambakkam, but these had to be closed despite their popularity.<ref>Young Men's Indian Association [http://www.ymiaindia.com/history.html# web page].</ref> | ||
[[File:YMIA 10-1-2014 celebration.jpg|350px|right|thumb|YMIA celebrating Annie Besant's birthday, October 1, 2014.]] | |||
== Activities == | == Activities == | ||
The organization has established a [https://www.facebook.com/pages/Young-Mens-Indian-Association/780448362021235 Facebook] page and is developing a member page with individual photos and email addresses. YMIA is seeking to launch affiliated branches in all major cities of India, with each having a lecture hall, gymnasium, library, reading room, recreation, and residences. Internships are offered to students who would like to develop a career in services and development of youth programs.<ref>Young Men's Indian Association [http://www.ymiaindia.com/history.html# web page].</ref> | |||
These are some reent activities and services of the YMIA | These are some reent activities and services of the YMIA: | ||
::* Sports, boxing, karate, and body building | ::* Sports, boxing, karate, and body building | ||
::* Fine arts competitions | ::* Fine arts competitions | ||
Latest revision as of 21:16, 31 March 2024
The Young Men's Indian Association (YMIA) is a youth organization that was founded by Annie Besant in 1914 in support of the Indian independence movement. In 1915 she built Gokhale Hall, named after Gopal Krishna Gokhale, so serve as its headquarters. YMIA continues to be a prominent institution in Chennai, offering Indian youth opportunities to improve in body, mind, moral character, and citizenship.[1][2] It offers recreational facilities, lectures, library and reading room, and residences. The YMIA has a web page and a presence in Facebook.
Early history
By 1914, Annie Besant had already been working for some years on establishment of schools and organizations to support Indian education and nationalism. In a 1908 address at Central Hindu College, she said, "Our work is the training of thousands of India's sons into noble manhood into worthiness to become free citizens in a free land." [3] Her political activity reached greatest intensity in the years 1914-1917. She worked with several other nationalist leaders to demand home rule for India, and formation of the YMIA was one aspect of this movement.
Mrs. Besant sponsored the construction of a building in Madras (now Chennai) for the YMIA, which was completed in 1915. A large public meeting hall in the building, designed to seat 1500 people, was given the name Gopal Krishna Gokhale Hall after the Indian leader. When she announced the formation of the Home Rule League in 1916, it was at Gokhale Hall. Many other nationalistic events took place there. The Indian Society of Oriental Art held an exhibition at the YMIA building in 1916, organized by Theosophist James Cousins.[4]
In his introduction to The Besant Spirit, George S. Arundale wrote of Dr. Besant's daily routine in Adyar during the time of her great activism in the Indian independence movement. Each evening at 5:30,
She would be seen having a cup of coffee at the Young Men's Indian Association, a fine building in Armenian Street given by herself to the youth of the city. It would have to be very important business which could cause her to forego this solemn and happy ritual. But often there was very important business. So many people had to be seen, committees to be attended, and above all those wonderful meetings in the Gokhale Hall, itself part of the Association premises. Most young people of to-day [note that this was written in 1939] are too young to remember those meetings of twenty years ago. The Hall packed to the brim with youth and a sprinkling of the older generation sedately seated on the platform. Enters the white-robed figure of the Editor of New India, almost gorgeously arrayed in silken sari, with an H. R. pendant in green and gold enamel – green and gold being the then Home Rule colours... A torrent of applause. A cheery smile... Wave upon wave of cheers. A bow to the audience with folded hands. A rustle of chairs and a general fussification as the entourage settled itself down. And then a Hall-wide hush of expectancy, with everybody impatient to hear the world's greatest orator demand freedom for India in language that no one could possibly mistake.[5]
Objects of the Association
According to its web page, the Association has these objects:
- To provide a building or buildings as a Young Men’s Club, with gymnasium, lecture hall, library, reading-room, recreation-rooms and residential quarters, mainly for students.
- To draw together students of all classes and creeds under a common roof so that they may recognize their common interests as citizens, to enable them to have lectures discussions and classes, and so to train and develop their bodies that they may grow into strong and healthy men.
- To do all such things as are incidental or conducive to the attainment of the above objects or any of them.
- To promote the physical, social, intellectual and well being of young people of all classes, creeds and communities, to undertake and conduct social service schemes, to provide, equip, conduct and maintain residential, educational and social institution, activities facilities and amenities for its members and others, to co-operate with other organizations working with similar objects for the welfare of humanity and to stimulate the development of movements for the higher advancement of society.
- To establish, equip maintain and conduct branches, departments, center, offices refreshment rooms, hostels boarding houses, tourist homes, homes for destitute children, libraries, reading and lecture rooms, congresses, conferences, study classes, canteen, gymnasium swimming pool, social service centers, educational or social institutions activities, functions works facilities and amenities which may be necessary or convenient for the advancement of the purpose or objects of the Association or for the advantage or convenient of its members and others connected with the Association but no intoxicants of any whatsoever shall be provided, used, sold kept or allowed in or upon any premises belonging to or in the occupation of the Association.
- To establish, provide, organize, maintain, supervise, control and conduct institution for the study and appreciation of indigenous and foreign languages and literature, are and science, studies research centers, laboratories, conferences and lecture halls, scientific, industrial and art exhibition, demonstrations, congresses and exchanges, art galleries, music and halls, television and dramatic performances, debates, symposia, concerts, sports and competitions and generally any undertaking, scheme work or activity whatsoever for the mental, moral or physical improve or benefit of the members or other connected with the Association.
- To provide, organize, equip maintain and conduct premises holding classes and competitions to arrange for and give prizes in respect thereof, delivery of lectures, giving of demonstrations and holding of other functions in connection with scientific and artistic subjects and for examinations and awards of diplomas and certificates and to institute, administer and undertake grants scholarships, rewards and other beneficiaries.
- To investigate, collect and circulate any knowledge or information on any subject deemed desirable to the purposes of the Association and to print, publish and issue journals, periodicals, books, leaflets, advertisements, reports, lectures and other reading matter which may be deemed useful or expedient for any such purpose.
- To solicit accept, hold and d\administer any donations, gifts legacies grants, subscription contributions or funds from members the public institutions, public trusts, universities, municipalities governments and other persons or bodies and whether subjects to any trust or otherwise for the furtherance of the objects of the Association.
- To promote education, research training and development on habit and human settlement, environment and other related issues of human value.
Governance
YMIA is a society registered under the provisions of Act 21 of 1860. Mr. R. Nataraj serves as President of the Governing body, which includes three Vice Presidents, Honorary Secretary, Honorary Treasurer, Honorary Join Secretary, and 17 members. In addition to an Executive Committee, there are committees for International YMIA Affiliation; Library and Internet; Gym and Sports; Students and Youth Activities; and Legal matters.
Facilities
YMIA has two locations in Chennai: the registered office at New India Buildings at No.49 Moore Street, and the administrative office at 54-57/2 Royapettah High Road in Mylapore. Gokhale Hall was partially demolished, but is now being renovated. Two hostels are now serving about 150 youth. Over the years additional hostels were operated in George town, Triplicane, Mylapore, and Nungambakkam, but these had to be closed despite their popularity.[6]
Activities
The organization has established a Facebook page and is developing a member page with individual photos and email addresses. YMIA is seeking to launch affiliated branches in all major cities of India, with each having a lecture hall, gymnasium, library, reading room, recreation, and residences. Internships are offered to students who would like to develop a career in services and development of youth programs.[7]
These are some reent activities and services of the YMIA:
- Sports, boxing, karate, and body building
- Fine arts competitions
- Carrom (a tabletop game) and chess
- Oratorical contests in 4 languages ( English, Tamil, Hindi, Telugu)
- Blood drive
- Republic Day celebrations
- Celebration of Swami Vivekananda's 150th birthday
- Memorial lectures and elocution contests honoring Dr. Annie Besant
- CDs of Annie Besant’s speeches
Notes
- ↑ YMIA web page
- ↑ Madras High Court document. 1962. Citation: AIR 1964 Mad 63, 1963 14 STC 1030 Mad Available at IndianKanoon.org.
- ↑ Annie Besant, The Besant Spirit Volume 7: The India that Shall Be: Articles from New India.
- ↑ Kathleen Taylor, Sir John Woodroffe Tantra and Bengal: 'An Indian Soul in a European Body?' (Surrey: Routledge, 2012), 70.
- ↑ George S. Arundale, Introduction to The Besant Spirit: Volume III Indian Problems (Adyar, Madras, India: Theosophical Publishing House, 1939), 13-14. The Besant Spirit is a compilation of writings by Annie Besant.
- ↑ Young Men's Indian Association web page.
- ↑ Young Men's Indian Association web page.