Antaḥkaraṇa: Difference between revisions
Pablo Sender (talk | contribs) |
Pablo Sender (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Antaḥkaraṇa''' (devanāgarī: अन्तःकरण) is a [[Sanskrit]] term that means "internal organ". In [[Hinduism|Hindu]] philosophy it refers to the totality of the mind, including the thinking faculty, memory, the sense of I-ness, and the discriminating faculty. | '''Antaḥkaraṇa''' (devanāgarī: अन्तःकरण) is a [[Sanskrit]] term that means "internal organ". In [[Hinduism|Hindu]] philosophy it refers to the totality of the mind, including the thinking faculty, memory, the sense of I-ness, and the discriminating faculty. | ||
In [[Theosophy]] the term is used with a special meaning that differs from Hindu one. According to [[Helena Petrovna Blavatsky|H. P. Blavatsky]], the antahkarana (also spelled by her as "antaskarana") is, figuratively speaking, the "bridge" that unites the lower and the higher [[Manas|mind]]. It is an aspect or function of the lower mind that retains its original purity. | |||
Antahkarana acts as a two-way communication through which the spiritual influence of the higher manas is conveyed to the personality, and all good and noble activity of the lower manas can reach the higher, to be assimilated in [[Devachan]]. | |||
== | ==General description== | ||
[[File:Antahkarana.JPG|right|200px|thumb|Graphic representation of the seven principles by H. P. Blavatsky. The antahkarana is the green line uniting the green downward triangle (lower manas) and the blue upward triangle (higher manas).]] | [[File:Antahkarana.JPG|right|200px|thumb|Graphic representation of the seven principles by H. P. Blavatsky. The antahkarana is the green line uniting the green downward triangle (lower manas) and the blue upward triangle (higher manas).]] | ||
In the [[Seven Principles#Seven principles in human beings|sevenfold constitution of human beings]] described in the Theosophical literature the fifth principle (counting from the physical body upwards) is called [[manas]], commonly translated as "mind". This principle is dual, comprising the higher mind (the spiritual mind, or [[Ego#Higher ego|reincarnating Ego]]), and the lower mind (the sensual mind, or the [[Ego#Lower ego|psychological ego]]). According to [[H. P. Blavatsky]], the | [[H. P. Blavatsky]], in [[The Theosophical Glossary (book)|''The Theosophical Glossary'']] defines it as follows: | ||
<blockquote>Antahkarana (Sk.)., or Antaskarana. The term has various meanings, which differ with every school of philosophy and sect. Thus Sankarâchârya renders the word as “understanding”; others, as “the internal instrument, the Soul, formed by the thinking principle and egoism”; whereas the Occultists explain it as the path or bridge between the Higher and the Lower Manas, the divine Ego, and the personal Soul of man. It serves as a medium of communication between the two, and conveys from the Lower to the Higher Ego all those personal impressions and thoughts of men which can, by their nature, be assimilated and stored by the undying Entity, and be thus made immortal with it, these being the only elements of the evanescent Personality that survive death and time. It thus stands to reason that only that which is noble, spiritual and divine in man can testify in Eternity to his having lived.<ref>Helena Petrovna Blavatsky, ''The Theosophical Glossary'' (Krotona, CA: Theosophical Publishing House, 1918), 22.</ref></blockquote> | |||
In the [[Seven Principles#Seven principles in human beings|sevenfold constitution of human beings]] described in the Theosophical literature the fifth principle (counting from the physical body upwards) is called [[manas]], commonly translated as "mind". This principle is dual, comprising the higher mind (the spiritual mind, or [[Ego#Higher ego|reincarnating Ego]]), and the lower mind (the sensual mind, or the [[Ego#Lower ego|psychological ego]]). According to [[H. P. Blavatsky]], antahkarana is the aspect of the lower mind that does not get entangled with kāma (the animal soul), thus acting as an "imaginary bridge" between the lower and higher [[ego]]s: | |||
<blockquote>The Antaskarana is therefore that portion of the Lower Manas which is one with the Higher, the essence, that which retains its purity; on it are impressed all good and noble aspirations, and in it are the upward energies of the Lower Manas, the energies and tendencies which become its Devachanic experiences. The whole fate of an incarnation depends on whether this pure essence, Antaskaraṇa, can restrain the Kāma-Manas or not. It is the only salvation. Break this and you become an animal.<ref>Helena Petrovna Blavatsky, ''Collected Writings XII, Instruction No. V'' (Wheaton, IL: Theosophical Publishing House, 1980), 710.</ref></blockquote> | <blockquote>The Antaskarana is therefore that portion of the Lower Manas which is one with the Higher, the essence, that which retains its purity; on it are impressed all good and noble aspirations, and in it are the upward energies of the Lower Manas, the energies and tendencies which become its Devachanic experiences. The whole fate of an incarnation depends on whether this pure essence, Antaskaraṇa, can restrain the Kāma-Manas or not. It is the only salvation. Break this and you become an animal.<ref>Helena Petrovna Blavatsky, ''Collected Writings XII, Instruction No. V'' (Wheaton, IL: Theosophical Publishing House, 1980), 710.</ref></blockquote> | ||
Revision as of 18:27, 24 April 2013
Antaḥkaraṇa (devanāgarī: अन्तःकरण) is a Sanskrit term that means "internal organ". In Hindu philosophy it refers to the totality of the mind, including the thinking faculty, memory, the sense of I-ness, and the discriminating faculty.
In Theosophy the term is used with a special meaning that differs from Hindu one. According to H. P. Blavatsky, the antahkarana (also spelled by her as "antaskarana") is, figuratively speaking, the "bridge" that unites the lower and the higher mind. It is an aspect or function of the lower mind that retains its original purity.
Antahkarana acts as a two-way communication through which the spiritual influence of the higher manas is conveyed to the personality, and all good and noble activity of the lower manas can reach the higher, to be assimilated in Devachan.
General description
H. P. Blavatsky, in The Theosophical Glossary defines it as follows:
Antahkarana (Sk.)., or Antaskarana. The term has various meanings, which differ with every school of philosophy and sect. Thus Sankarâchârya renders the word as “understanding”; others, as “the internal instrument, the Soul, formed by the thinking principle and egoism”; whereas the Occultists explain it as the path or bridge between the Higher and the Lower Manas, the divine Ego, and the personal Soul of man. It serves as a medium of communication between the two, and conveys from the Lower to the Higher Ego all those personal impressions and thoughts of men which can, by their nature, be assimilated and stored by the undying Entity, and be thus made immortal with it, these being the only elements of the evanescent Personality that survive death and time. It thus stands to reason that only that which is noble, spiritual and divine in man can testify in Eternity to his having lived.[1]
In the sevenfold constitution of human beings described in the Theosophical literature the fifth principle (counting from the physical body upwards) is called manas, commonly translated as "mind". This principle is dual, comprising the higher mind (the spiritual mind, or reincarnating Ego), and the lower mind (the sensual mind, or the psychological ego). According to H. P. Blavatsky, antahkarana is the aspect of the lower mind that does not get entangled with kāma (the animal soul), thus acting as an "imaginary bridge" between the lower and higher egos:
The Antaskarana is therefore that portion of the Lower Manas which is one with the Higher, the essence, that which retains its purity; on it are impressed all good and noble aspirations, and in it are the upward energies of the Lower Manas, the energies and tendencies which become its Devachanic experiences. The whole fate of an incarnation depends on whether this pure essence, Antaskaraṇa, can restrain the Kāma-Manas or not. It is the only salvation. Break this and you become an animal.[2]
The antaḥkaraṇa in Theosophy is not seen as a structural principle but as a temporary function, active when the lower mind aspires towards the higher:
Q. The Antahkarana is the link between the Higher and the Lower Egos; does it correspond to the umbilical cord in projection?
A. No; the umbilical cord joining the astral to the physical body is a real thing. Antahkarana is imaginary, a figure of speech, and is only the bridging over from the Higher to the Lower Manas. Antahkarana only exists when you commence to “throw your thought upwards and downwards.” The Mâyâvi Rûpa, or Mânasic body, has no material connection with the physical body, no umbilical cord.[3]
In order not to confuse the mind of the student with the abstruse difficulties of Indian metaphysics, let him view the lower Manas or Mind, as the personal Ego during the waking state, and as Antaskaraṇa only during those moments when it aspires towards its higher half, and thus becomes the medium of communication between the two. It is for this reason that it is called “Path.”[4]
Antaḥkaraṇa can then be seen as a path that has to be trodden by developing spiritual qualities. A connection has been suggested between the "Portals" in the book The Voice of the Silence and the different "divisions" of the antaḥkaraṇa:
Q. We are told in The Voice of the Silence that we have to become “the path itself,” and in another passage that Antahkarana is that path. Does this mean anything more than that we have to bridge over the gap between the consciousness of the Lower and the Higher Egos?
A. That is all.
Q. We are told that there are seven portals on the Path: is there then a sevenfold division of Antahkarana? Also, is Antahkarana the battlefield?
A. It is the battlefield. There are seven divisions in the Antahkarana. As you pass from each to the next you approach the Higher Manas. When you have bridged the fourth you may consider yourself fortunate.[5]
According to the Law of Correspondences there is a correlation between inner principles and outer organs. Within the human brain, it is said that the pituitary gland or hypophysis is connected to antaḥkaraṇa:
The fourth of these cavities is the Pituitary Body, which corresponds with Manas-Antaskaraṇa, the bridge to the Higher Intelligence; it contains various essences.[6]
According to G. de Purucker
In his Occult Glossary, Gottfried de Purucker uses the word antaḥkaraṇa in a wider sense than the way H. P. Blavatsky did:
Antaskaraṇa (Sanskrit) Perhaps better spelled as antaḥkaraṇa. A compound word: antar, "interior," "within"; karaṇa, sense organ. Occultists explain this word as the bridge between the higher and lower manas or between the spiritual ego and personal soul of man. Such is H. P. Blavatsky's definition. As a matter of fact there are several antaḥkaraṇas in the human septenary constitution - one for every path or bridge between any two of the several monadic centers in man. Man is a microcosm, and therefore a unified composite, a unity in diversity; and the antaḥkaraṇas are the links of vibrating consiousness-substance uniting these various centers.[7]
In Hinduism
In Hindu philosophy, the antahkarana (Skt., often translated as the "internal organ") refers to the psychological apparatus of the individual. In the Vedāntic literature, the antahkaraṇa is organised into four parts:
- Ahamkāra (ego) — the origin to the psychological 'I' associated to the body and its senses.
- Buddhi (intellect) — the principle that is able to discern truth from falsehood and thereby to make wisdom possible.
- Manas (mind) — the faculty of doubt and volition; the lower or instinctive mind, seat of desire and governor of sensory and motor organs.
- Citta (memory) — the part that deals with remembering and forgetting
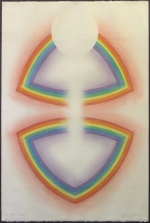
Artistic representations
Theosophical artist Burton Callicott created a beautiful rendition of this concept in his pastel Antahkarana. It hangs by the Meditation Room in the L. W. Rogers Building at the Theosophical Society in America headquarters.
Notes
- ↑ Helena Petrovna Blavatsky, The Theosophical Glossary (Krotona, CA: Theosophical Publishing House, 1918), 22.
- ↑ Helena Petrovna Blavatsky, Collected Writings XII, Instruction No. V (Wheaton, IL: Theosophical Publishing House, 1980), 710.
- ↑ Helena Petrovna Blavatsky, The Esoteric Writings of Helena Petrovna Blavatsky, (Wheaton, IL: Theosophical Publishing House, 1980), 428.
- ↑ Helena Petrovna Blavatsky, Collected Writings XII, Instruction No. III (Wheaton, IL: Theosophical Publishing House, 1980), 633.
- ↑ Helena Petrovna Blavatsky, The Esoteric Writings of Helena Petrovna Blavatsky, (Wheaton, IL: Theosophical Publishing House, 1980), 428.
- ↑ Helena Petrovna Blavatsky, Collected Writings XII, Instruction No. V (Wheaton, IL: Theosophical Publishing House, 1980), 697.
- ↑ Gottfried de Purucker, Occult Glossary (Pasadena, CA: Theosophical University Press, 1996), 5.
Additional resources
- Antaḥkaraṇa at Theosopedia