Koot Hoomi: Difference between revisions
m (Corrected "Mrs. Mrs. Mary Hollis Billings" to "Mrs. Mary Hollis Billings".) |
Pablo Sender (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
In another letter, Mme. Blavatsky writes: | In another letter, Mme. Blavatsky writes: | ||
<blockquote>Koot Hoomi awoke from his Samadhi on December 24th [1881]. On the 1st of January [1882], he communicated with us, and is now teaching Mr. Sinnett philosophy again.</blockquote> | <blockquote>Koot Hoomi awoke from his Samadhi on December 24th [1881]. On the 1st of January [1882], he communicated with us, and is now teaching Mr. Sinnett philosophy again.<ref>From an unpublished letter found by Daniel Caldwell, preserved in the archives of Brigham Young University in Utah.</ref></blockquote> | ||
== Writings == | == Writings == | ||
Revision as of 20:33, 12 April 2021

Koot Hoomi (also spelled Kuthumi, and frequently referred to simply as K.H.) is one of the Mahatmas that inspired the founding of the Theosophical Society. He engaged in a correspondence with two English Theosophists living in India, A. P. Sinnett and A. O. Hume, correspondence was published in the book The Mahatma Letters to A. P. Sinnett.
Personal features
Few descriptive references to K.H. occur in The Mahatma Letters to A. P. Sinnett and the writings of Mme. Blavatsky. The name Koot Hoomi seems to be a pseudonym. We find a reference to a "Rishi Kuthumi" in several Puranas, as for example in the Vishnu Purana (Book 3, Chapter 6) where he is said to be a pupil of Paushyinji. In reference to this Mme. Blavatsky wrote:
The name of Rishi Koothumi is mentioned in more than one Purana, and his Code is among the 18 Codes written by the various Rishis and preserved at Calcutta in the library of the Asiatic Society. But we have not been told whether there is any connection between our Mahatma of that name, and the Rishi, and we do not feel justified in speculating upon the subject. All we know is, that both are Northern Brahmans, while the Môryas are Kshatriyas.[1]
K.H.'s early letters to Sinnett are signed with the name Koot Hoomi Lal Sing. However, later in the correspondence, he says the "Lal Singh" was an addition made by his disciple Djwal Khool:
Why have you printed the Occult World before sending it to me for revision? I would have never allowed the passage to pass; nor the "Lal Sing" either foolishly invented as half a nom de plume by Djwal K. and carelessly allowed by me to take root without thinking of the consequences. . .[2]
The word "Lal" is mostly used in Chitral (now in Pakistan) as surname or "Title name", meaning "Tribe Chief". "Singh" is a common title, middle name, or surname originally used by the Hindu Kshatriyas (warriors and kings). It is used as a surname or middle name by Sikhs, and Hindu communities like Rajputs, Marathas, Jats, Yadavs and Ahirs among other.
In an interview by Charles Johnston to H. P. Blavatsky, he described the handwriting of Master K.H. in the following way:
. . . evidently a man of very gentle and even character, but of tremendously strong will; logical, easy-going, and taking endless pains to make his meaning clear. It was altogether the handwriting of a cultivated and very sympathetic man.[3]
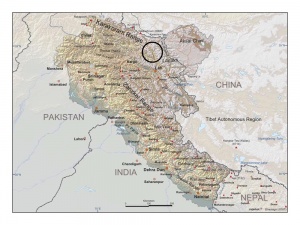
Master KH is said to live in a house in a ravine in Tibet, near the house of Master Morya. In 1881, Colonel Henry S. Olcott wrote to A. O. Hume:
I have also personally known [Master Koot Hoomi] since 1875. He is of quite a different, a gentler, type, yet the bosom friend of the other [Master Morya]. They live near each other with a small Buddhist Temple about midway between their houses. In New York, I had . . . a colored sketch on China silk of the landscape near [Koot Hoomi]'s and my Chohan's residences with a glimpse of the latter’s house and of part of the little temple.[4]
Mme. Blavatsky, in a letter to Mrs. Hollis Billings wrote:
Now Morya lives generally with Koot-Hoomi who has his house in the direction of the Kara Korum [Karakoram] Mountains, beyond Ladak, which is in Little Tibet and belongs now to Kashmire. It is a large wooden building in the Chinese fashion pagoda-like, between a lake and a beautiful mountain. . . .[5]
This is confirmed by a reference given by Mahatma K. H. himself, in a letter to A. P. Sinnett:
I was coming down the defiles of Kouenlun — Karakorum you call them . . . and was crossing over to Lhadak on my way home.[6]
Account by C. W. Leadbeater
C. W. Leadbeater described the physical appearance of Master KH in this way:
The Master Kuthumi wears the body of a Kashmiri Brahman, and is as fair in complexion as the average Englishman. He, too, has flowing hair, and His eyes are blue and full of joy and love. His hair and beard are brown, which, as the sunlight catches it, becomes ruddy with glints of gold. His face is somewhat hard to describe, for His expression is ever changing as He smiles; the nose is finely chiselled, and the eyes are large and of a wonderful liquid blue.[7]
Education in Europe
Apparently before being an Adept, Master Koot Hoomi visited Europe and studied in some of the Universities there. Mme. Blavatsky said that Mahatma K.H. "is a Kashmiri Brahman by birth . . . and has travelled a good deal in Europe."[8]
Mr. A. O. Hume, in his "Hints on Esoteric Theosophy," wrote:
Take a case said to have occurred many years ago in Germany, in which a Brother, who has corresponded with us, is said to have taken part. He was at this time a student, and though in course of preparation was not then himself an Adept, but was, like all regular chelas, under the special charge of an Adept. A young friend of his was accused of forgery, and tried for the same. Our Brother, then a student as above explained, was called as a witness to prove his friend's handwriting; the case was perfectly clear and a conviction certain. Through his mentor, our Brother learnt that his accused friend did not really deserve punishment that would necessarily fall on him, and which would have ruined not only him, but other innocent persons dependent on him. He had really committed a forgery but not knowingly or meaningly, though it was impossible to show this. So when the alleged forged document was handed to the witness, he merely said: "I see nothing written here," and returned the deed blank. His mentor had caused the entire writing to disappear. It was supposed that a wrong paper had been by mistake handed to the witness; search was made high and low, but the deed never appeared, and the accused was perforce acquitted.[9]
Maybe it is because of this that the Master Morya refers to K.H. as "a fine scholar".[10] Master K.H. speaks English and French well, which in one letter led Master M. to call him "Frenchified". [11]. He probably knew German also.
In a letter received by Mr. Sinnett on July 5, 1881, Master K.H. wrote:
I may answer you, what I said to G. H. Fechner one day, when he wanted to know the Hindu view on what he had written — "You are right;... ‘every diamond, every crystal, every plant and star has its own individual soul, besides man and animal...’ and, ‘there is a hierarchy of souls from the lowest forms of matter up to the World Soul,’ but you are mistaken when adding to the above the assurance that ‘the spirits of the departed hold direct psychic communication with Souls that are still connected with a human body’ — for, they do not."[12]
In 1883, C. C. Massey, leader of the British Theosophists, tried to test this evidence of the existence of the Mahatmas by writing to Dr. Hugo Wernekke, who lived at Weimar, Germany, and was in touch with a Professor Gustav T. Fechner. He wanted "to find out whether Professor Fechner ever had such a conversation with an Oriental." The answer from Professor G. T. Fechner to Dr. Hugo Wernekke dated "Leipzig, April 25th, 1883" said:
What Mr. Massey enquires about is undoubtedly in the main correct; the name of the Hindu concerned, when he was in Leipzig, was however, Nisi Kanta Chattopadhyaya, not Koot Humi. In the middle of the seventies he lived for about one year in Leipzig and aroused a certain interest owing to his foreign nationality, without being otherwise conspicuous; he was introduced to several families and became a member of the Academic Philosophical Society, to which you also belonged, where on one occasion he gave a lecture on Buddhism.[13]
C. C. Massey wrongly assumed that Nisi Kanta Chattopadhyaya was a pseudonym used by Master K.H., although the former was well-known Indian gentleman.
Travels
Koot Hoomi traveled widely, as documented by Mary K. Neff:[14]
- 1870s - student in Europe - Leipzig, Zurich, Wurzburg
- 1880 - Toling, in western Tibet; Kashmir; Karakorum, in Mongolia
- 1881 - Tirich Mir, a mountain in the Hindu Kush range; Sakkya-Jung, Ghalaring-Tho Lamasery, and Horpa Pa La, in unknown territory
- 1882 - Unknown location of KH's retreat; Himalayan lamasery near Darjeeling
- 1883 - extended tour of Asia; Lake Manasarovara in the Himalayas; Lahore; Kashmir; Madras; Singapore; Ceylon; Burma; Mysore; Sanangerri (unknown location); China; Cambodia
Travel was difficult. KH wrote in Mahatma Letter No. 20, "I hope these disjointed reflections may be pardoned in one who remained for over nine days in his stirrups without dismounting."
K.H.'s retreat and initiation
On Oct 2, 1881, Mme. Blavatsky described this to Mrs. Hollis Billings as follows:
K. H. or Koot-Hoomi is now gone to sleep for three months to prepare during this Sumadhi or continuous trance state for his initiation, the last but one, when he will become one of the highest adepts. Poor K. H. his body is now lying cold and stiff in a separate square building of stone with no windows or doors in it, the entrance to which is effected through an underground passage from a door in Toong-ting (reliquary, a room situated in every Thaten (temple) or Lamisery; and his Spirit is quite free. An adept might lie so for years, when his body was carefully prepared for it beforehand by mesmeric passes etc. It is a beautiful spot where he is now in the square tower. The Himalayas on the right and a lovely lake near the lamisery. His Cho-han (spiritual instructor, master, and the Chief of a Tibetan Monastery takes care of his body. M . . also goes occasionally to visit him. It is an awful mystery that state of cataleptic sleep for such a length of time. . .[15]
Master Morya in a letter to A. P. Sinnett described K.H.'s retreat as follows:
At a certain spot not to be mentioned to outsiders, there is a chasm spanned by a frail bridge of woven grasses and with a raging torrent beneath. The bravest member of your Alpine clubs would scarcely dare to venture the passage, for it hangs like a spider’s web and seems to be rotten and impassable. Yet it is not; and he who dares the trial and succeeds — as he will if it is right that he should be permitted — comes into a gorge of surpassing beauty of scenery — to one of our places and to some of our people, of which and whom there is no note or minute among European geographers. At a stone’s throw from the old Lamasery stands the old tower, within whose bosom have gestated generations of Bodhisatwas. It is there, where now rests your lifeless friend — my brother, the light of my soul, to whom I made a faithful promise to watch during his absence over his work.[16]
In another letter, Mme. Blavatsky writes:
Koot Hoomi awoke from his Samadhi on December 24th [1881]. On the 1st of January [1882], he communicated with us, and is now teaching Mr. Sinnett philosophy again.[17]
Writings
K.H. was an excellent writer. In addition to his extensive correspondence, he provided articles and guidance to several periodicals.
Letters written by K.H.
K. H. had the assignment to educate two English Theosophists living in India, A. P. Sinnett and A. O. Hume, and this primarily took the form of correspondence that was published in the book The Mahatma Letters to A. P. Sinnett. In addition, letters to H. P. Blavatsky, Colonel Olcott, and many others were published in Letters from the Masters of the Wisdom.
For a list of Master K. H.'s letters that were published in these sources, see Category:ML from Koot Hoomi. There are 195 letters in all, which were typically written in blue ink. His writing demonstrates a wide knowledge of religion, science, literature, and current affairs, and frequently includes phrases in Latin and French.
Involvement in periodicals
He took a keen interest in The Theosophist, and wrote many articles. He "exercised a constant and varied supervision, from proof reading to furnishing material for articles and substance for replies to enquiring or controversial letters, when not writing them himself."[18] KH was also heavily involved in planning for the establishment of A. P. Sinnett's proposed daily Indian newspaper, The Phoenix, but funding for the venture was never sufficient.
Samples of signature
Initials from Mahatma Letter No. 74
Initials from Mahatma Letter No. 98
Signature from Mahatma Letter No. 2
Signature from Mahatma Letter No. 9
Online resources
Articles
- Where was the "Ravine in Tibet"? by Daniel H. Caldwell
- K.H. and the Kadampas by Jacques Mahnich
- Echoes of the Past: Master Koot Hoomi by Mary K. Neff
Notes
- ↑ H. P. Blavatsky, Collected Writings vol. VI, (Adyar, Madras: Theosophical Publishing House, 1979), 41.
- ↑ Vicente Hao Chin, Jr., ed., Mahatma Letters to A. P. Sinnett in Chronological Sequence No. 136, (Quezon City, Phillipines: Theosophical Publishing House, 1993), 450. See Mahatma Letter No. 136 page 10.
- ↑ H. P. Blavatsky, Collected Writings vol. VIII, (Adyar, Madras: Theosophical Publishing House, 1979), 399.
- ↑ A. O. Hume, Hints on Esoteric Theosophy vol. 1 (Bombay, India: The Theosophical Society, 1882), 83.
- ↑ H. P. Blavatsky, The Theosophical Forum (May, 1936), 345.
- ↑ Vicente Hao Chin, Jr., The Mahatma Letters to A.P. Sinnett in Chronological Sequence No. 5 (Quezon City: Theosophical Publishing House, 1993), 15. See Mahatma Letter No. 5 page 2.
- ↑ C. W. Leadbeater, The Masters and the Path (Chicago: Theosophical Press, 1925), 38.
- ↑ H. P. Blavatsky, Collected Writings vol. VIII, (Adyar, Madras: Theosophical Publishing House, 1979), 399.
- ↑ A. O. Hume, Hints on Esoteric Theosophy vol. 1 (Bombay, India: The Theosophical Society, 1882), 29.
- ↑ Vicente Hao Chin, Jr., ed., Mahatma Letters to A. P. Sinnett in Chronological Sequence No. 29, (Quezon City, Phillipines: Theosophical Publishing House, 1993), 86. See Mahatma Letter No. 29 page 1.
- ↑ Vicente Hao Chin, Jr., ed., Mahatma Letters to A. P. Sinnett in Chronological Sequence No. 26, (Quezon City, Phillipines: Theosophical Publishing House, 1993), 83. See Mahatma Letter No. 26 page 1.
- ↑ Vicente Hao Chin, Jr., ed., Mahatma Letters to A. P. Sinnett in Chronological Sequence No. 18, (Quezon City, Phillipines: Theosophical Publishing House, 1993), 63. See Mahatma Letter No. 18 page 13-14.
- ↑ See "Echoes of the Past: Master Koot Hoomi" by Mary K. Neff at http://www.blavatskyarchives.com/neffkoothoomi.htm
- ↑ Mary K. Neff, The "Brothers" of Madame Blavatsky (Adyar, Madras, India: Theosophical Publishing House, 1932), 63-79. Quoting from Introduction to Letters of H. P. Blavatsky to A. P. Sinnett, The Mahatma Letters to A. P. Sinnett, and other sources.
- ↑ H. P. Blavatsky, The Theosophical Forum (Point Loma, California: May 1936), 345.
- ↑ Vicente Hao Chin, Jr., ed., Mahatma Letters to A. P. Sinnett in Chronological Sequence No. 29, (Quezon City, Phillipines: Theosophical Publishing House, 1993), 87. See Mahatma Letter No. 29 page 4.
- ↑ From an unpublished letter found by Daniel Caldwell, preserved in the archives of Brigham Young University in Utah.
- ↑ Mary K. Neff, The "Brothers" of Madame Blavatsky (Adyar, Madras, India: Theosophical Publishing House, 1932), 22. See Chapter III, pages 22-33.